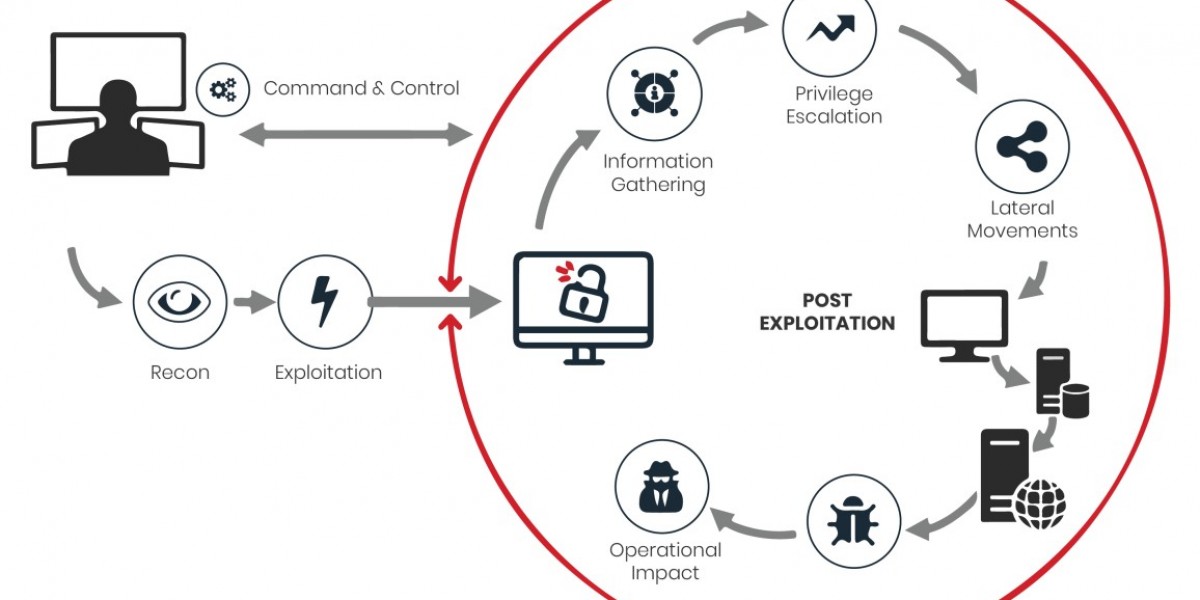
Understanding Breach and Attack Simulation (BAS)
Breach and Attack Simulation is an advanced cybersecurity testing method that continuously simulates real-world cyber threats in a controlled manner. Unlike traditional penetration testing, BAS automates attack scenarios based on the latest threat intelligence. It helps organizations evaluate the effectiveness of their security controls and identify gaps proactively. By mimicking various attack vectors such as phishing, malware injection, and lateral movement, BAS enables a comprehensive assessment without harming actual systems. These simulations offer crucial visibility into vulnerabilities, empowering IT teams to fine-tune defenses before real attackers strike. BAS is rapidly becoming a foundational element in security validation, offering actionable insights and ensuring businesses remain a step ahead of evolving threats. The result is a stronger, more resilient cybersecurity posture.
Key Benefits of Implementing BAS Tools
Implementing Breach and Attack Simulation tools offers numerous benefits for cybersecurity teams. First, it allows for continuous security validation, ensuring that defenses are actively working against the latest threats. BAS tools identify configuration issues, security blind spots, and policy misalignments in real time. These simulations also support compliance efforts by providing documented evidence of testing and remediation. Moreover, automated testing saves time and resources compared to manual penetration testing. Organizations can test across networks, endpoints, and cloud environments without interrupting business operations. By offering repeatable and scalable testing scenarios, BAS tools ensure rapid feedback and streamlined incident response. Ultimately, BAS improves threat readiness, reduces risk exposure, and strengthens decision-making for security investments. It aligns security strategies with actual threat behavior.
How BAS Works: Simulating Real-World Threats
BAS platforms work by emulating the tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs) used by cybercriminals. These simulations are based on frameworks like MITRE ATT&CK to ensure alignment with real-world adversarial behavior. Once deployed, BAS tools conduct controlled attacks across various layers—email, endpoints, servers, and network infrastructure. They test for vulnerabilities such as open ports, weak configurations, unpatched systems, and poor access controls. Simulations may include phishing emails, lateral movement, privilege escalation, and ransomware deployment. Results are collected and analyzed to show which defenses worked and where breakdowns occurred. This insight allows cybersecurity teams to prioritize patches, reconfigure settings, and improve detection mechanisms. Importantly, these tests are non-disruptive and safe for live environments. They are designed for repeat use, enabling ongoing security assessments.
Choosing the Right BAS Platform for Your Needs
Selecting the right BAS platform involves evaluating features, scalability, integration, and threat intelligence capabilities. Start by identifying your organization's specific security goals and infrastructure complexity. Look for BAS tools that align with your environment—whether on-premises, cloud-based, or hybrid. Ideal platforms offer comprehensive coverage across endpoints, networks, and identity systems. Integration with existing security tools like SIEM, SOAR, and EDR enhances value and automation. Leading BAS platforms provide customizable attack scenarios, intuitive dashboards, and detailed remediation guidance. Regular updates and access to a global threat database are essential to stay current. Additionally, consider platforms that support compliance reporting and role-based access for collaboration across teams. A pilot deployment or trial period is helpful for evaluating performance. The right tool ensures continuous, effective security validation.
BAS vs. Penetration Testing: Key Differences
While both BAS and penetration testing aim to uncover security gaps, they differ in scope, frequency, and automation. Penetration testing is typically manual and performed periodically—often annually—to meet compliance or audit requirements. It provides deep insights but is limited in frequency and coverage. In contrast, BAS is an automated and continuous process that runs 24/7 in live environments without disrupting operations. BAS provides constant validation against emerging threats, offering broader, more scalable assessments. It simulates attacker behavior based on real threat intelligence, giving security teams daily feedback. While pen testing is ideal for in-depth, targeted reviews, BAS is best for ongoing monitoring and rapid detection of vulnerabilities. Together, they provide a comprehensive security strategy when used in tandem, covering both depth and breadth.
Real-World Applications and Use Cases
Breach and Attack Simulation is widely adopted across industries to strengthen cybersecurity readiness. Financial institutions use BAS to test defenses against phishing and banking malware. Healthcare organizations simulate ransomware and insider threats to protect sensitive patient data. Government agencies rely on BAS for compliance and critical infrastructure protection. In the tech sector, BAS supports DevSecOps by validating security early in the software development lifecycle. Managed security providers use BAS tools to demonstrate value and ensure service effectiveness for clients. Additionally, companies use BAS to prepare for audits, train security teams, and test incident response plans. The ability to safely replicate attack scenarios empowers organizations to understand real risk exposure. These simulations bridge the gap between theory and practice in cybersecurity operations.
Future of BAS: AI Integration and Threat Intelligence
The future of Breach and Attack Simulation lies in AI integration and real-time threat intelligence. Modern BAS platforms are incorporating machine learning to adapt simulations based on user behavior and environment changes. AI-driven BAS can identify evolving attack patterns, predict vulnerabilities, and optimize testing paths. Integration with threat intelligence feeds ensures simulations stay relevant with global attack trends. BAS tools are becoming more intelligent, self-tuning, and predictive. Cloud-native BAS solutions are also emerging, allowing scalable testing across complex hybrid architectures. As cybersecurity threats become more sophisticated, BAS will evolve into a proactive defense mechanism, blending automation, intelligence, and contextual risk analysis. Continuous innovation in BAS ensures it remains a critical asset in the cybersecurity ecosystem—enhancing resilience and threat preparedness for the digital age.