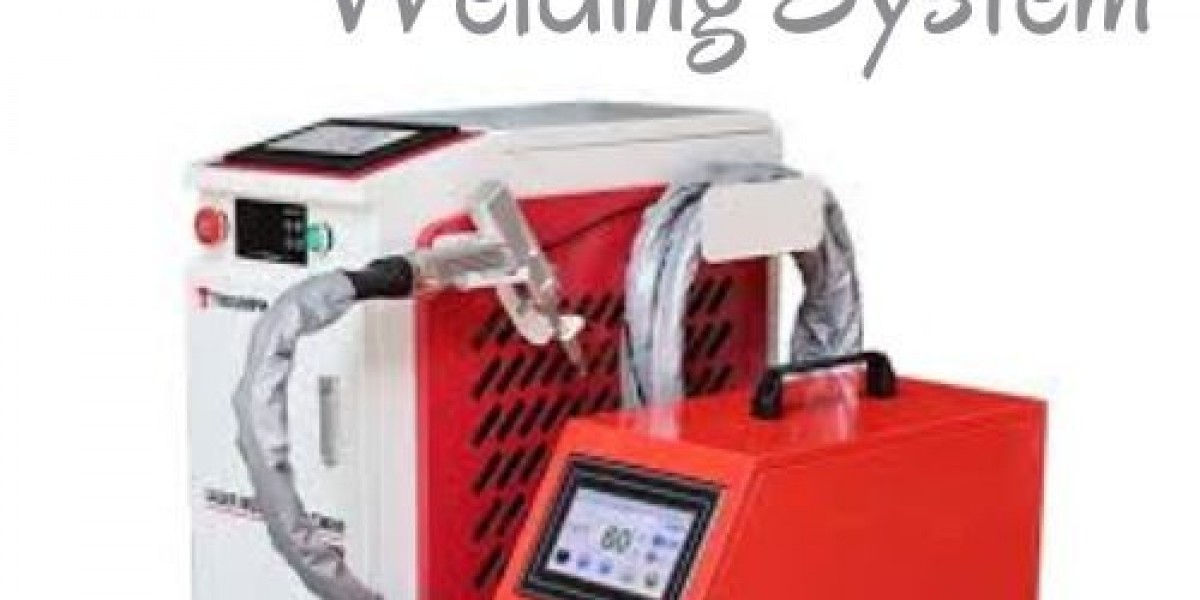
A laser welding system represents a modern approach to metal joining that aligns with the evolving demands of industrial production, precision engineering, and advanced fabrication environments. This system is designed to deliver controlled energy through a concentrated laser beam, enabling seamless fusion of metals with exceptional accuracy. Across global manufacturing sectors, the laser welding system has become an essential part of automated and semi-automated production lines, supporting consistent quality, repeatable performance, and scalable operations.
The foundation of a laser welding system lies in its ability to generate a focused laser beam that interacts directly with the material surface. When the beam contacts the metal, it produces localized heat sufficient to create a weld pool, allowing materials to merge at a molecular level. This process is widely applied to metals such as stainless steel, carbon steel, aluminum, copper, titanium, and various metal alloys. The controlled nature of the beam allows manufacturers to maintain precise weld seams even on thin or complex components.
In industrial environments, a laser welding system is commonly integrated into robotic arms, CNC machines, or automated production cells. This integration supports high-speed welding tasks that require accuracy and repeatability. Automotive manufacturing relies heavily on laser welding system installations for body structures, battery components, exhaust systems, and powertrain assemblies. The consistency achieved through automation ensures uniform weld quality across large production volumes without deviation.
A laser welding system also plays a vital role in electronics and electrical component manufacturing. Miniaturized parts, delicate connectors, and fine conductive materials demand precise joining without excessive heat exposure. Laser-based welding supports these requirements by allowing highly controlled energy input, making it suitable for micro-welding applications. Medical device manufacturing similarly depends on laser welding system technology for assembling surgical tools, implants, and diagnostic equipment where cleanliness and precision are essential.
In aerospace and defense sectors, the laser welding system supports complex fabrication processes involving high-performance materials. Aircraft structures, turbine components, fuel systems, and structural reinforcements require strong, consistent welds that meet strict regulatory standards. Laser welding enables manufacturers to achieve uniform seams on complex geometries while maintaining strict dimensional tolerances. The technology is well suited for both prototype development and full-scale production.
A modern laser welding system is often paired with advanced control software that allows operators to adjust parameters such as beam intensity, pulse duration, welding speed, and focal position. These controls enable customization of welding processes according to material thickness, joint configuration, and production requirements. Data monitoring and process logging further support quality assurance and traceability, which are critical in regulated industries.
The flexibility of a laser welding system allows it to be used in both manual and automated workflows. Handheld configurations are commonly used for maintenance, repair, and small-scale fabrication tasks, while fully automated systems dominate large industrial settings. This adaptability makes laser welding system solutions suitable for workshops, factories, and specialized production facilities alike.
Another important aspect of a laser welding system is its compatibility with modern manufacturing trends such as Industry 4.0 and smart factories. Many systems are designed to integrate with digital production environments, enabling real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and seamless communication with other manufacturing equipment. This connectivity enhances production efficiency and supports long-term operational planning.
In metal fabrication and custom manufacturing, a laser welding system enables the creation of clean, aesthetically refined weld seams. Architectural metalwork, decorative panels, frames, and custom enclosures benefit from the precision and control offered by laser welding. The ability to produce uniform seams enhances the visual appeal of finished products, which is especially valuable in high-end commercial and residential applications.
A laser welding system is also widely used in tool and mold manufacturing. Precision molds, dies, and tooling components often require repair or modification during their lifecycle. Laser welding allows localized material addition and restoration without affecting surrounding areas. This capability supports tool longevity and reduces downtime in production environments where molds and dies are critical assets.
From a production planning perspective, the laser welding system supports streamlined workflows by reducing the need for extensive post-weld processing. Consistent seam formation and controlled heat input help maintain component geometry, which is essential for assemblies that require tight tolerances. This reliability contributes to smoother downstream operations such as machining, coating, or assembly.
In renewable energy industries, the laser welding system contributes to the fabrication of components used in solar panels, wind turbines, and energy storage systems. Battery manufacturing, in particular, relies on laser welding for cell connections, busbars, and casing assemblies. The precision and repeatability of the laser welding system align with the strict quality requirements of energy storage technologies.
The adoption of a laser welding system also reflects a commitment to modern manufacturing standards. As industries continue to evolve toward higher efficiency and smarter production methods, laser-based welding solutions are increasingly viewed as a long-term investment. Their ability to support diverse applications, materials, and production scales makes them relevant across multiple industrial sectors.
In research and development environments, a laser welding system is frequently used for prototyping and material testing. Engineers and designers can experiment with different joint designs, materials, and configurations while maintaining precise control over welding conditions. This capability accelerates innovation and supports the development of new products and manufacturing techniques.
Global demand for laser welding system technology continues to grow as manufacturers seek reliable solutions that align with automation, quality control, and advanced fabrication requirements. From small workshops to large-scale industrial plants, the laser welding system has established itself as a cornerstone of modern metal joining. Its presence across diverse industries highlights its versatility and importance in contemporary manufacturing landscapes.
By supporting precision, scalability, and integration with automated systems, the laser welding system remains a central component in the evolution of industrial production. As materials, designs, and manufacturing expectations continue to advance, the laser welding system stands as a dependable solution for meeting complex welding demands in a wide range of professional applications.