The field of urinary stone treatment continues to evolve, and electrohydraulic lithotripsy has become the mainstream clinical choice due to its high efficiency, safety, and low damage. As a medical company, how can you quickly seize the technology dividend? Core technology module development capabilities + flexible production solutions may be the key to breaking through.
Clinical Needs Drive Technology Upgrades
Clinical Challenges
Traditional lithotripsy equipment has problems such as low energy control accuracy, risk of postoperative complications, and insufficient clearance rate of complex stones
Technical Breakthroughs
New generation pulse waveform optimization technology (reduces the risk of tissue thermal damage)
Intelligent impedance matching system (dynamically adjusts energy output to improve lithotripsy efficiency)
Miniaturized electrode design (adapted to minimally invasive scenarios such as ureteroscopes)
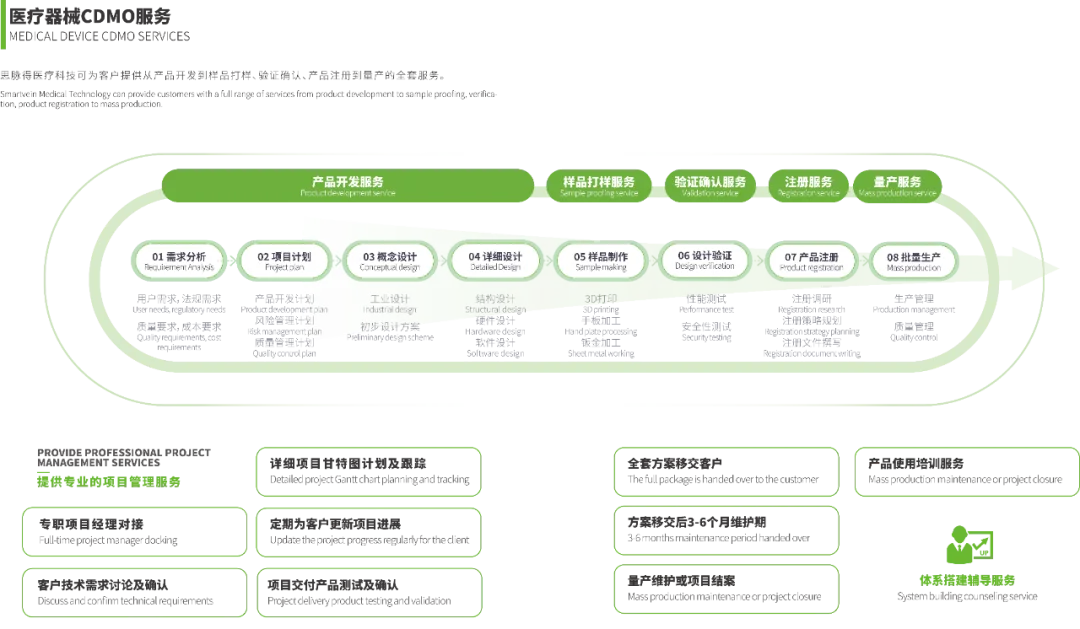
From "Single Production" To "Full-Link Technology Empowerment"
Core Module Customization and Development
Electrodes and Pulse Generators: Provide different power/size/wear resistance level solutions to match the needs of multiple scenarios in urology/hepatobiliary surgery
Intelligent Safety System: Integrated temperature monitoring and energy feedback control modules to reduce equipment operation risks

Flexible Production Support
Quick Response Mechanism: Support small-batch trial production to large-scale delivery, helping customers shorten product launch cycle
Full-Process Quality Control System: ISO 13485 certified production line + Shock wave energy stability test platform to ensure batch consistency

Full-Cycle Technology Collaboration/CDMO
Clinical Pain Point Transformation: Jointly conduct doctor interviews → Technical solution optimization → Animal experiment verification closed loop
Registration Application Support: Provide electrical safety/EMC/biocompatibility test report templates to accelerate the evidence collection process
How to Apply the Technical Solution?
Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography (ERCP)
Application Scenario: Mainly used to treat common bile duct stones, especially impacted stones or large stones that are difficult to remove with traditional stone baskets.
Operation Method: Send the liquid electrolithotomy electrode into the bile duct through the working channel of the duodenoscope, discharge at the stone under direct vision, and the stone can be directly removed through the stone basket after crushing.
Advantages: No need to rely on the choledochoscope, integrated lithotripsy and stone removal, high efficiency.
Percutaneous Transhepatic Choledochoscopy Lithotripsy (PTCS)
Application Scenario: Applicable to difficult-to-remove stones in the intrahepatic bile duct, especially residual stones after surgery or cases that cannot be treated through the T-tube sinus.
Operation Method: After percutaneous puncture to establish a channel, insert the choledochoscope to the stone site, and directly crush the stone through the liquid electrolithotomy electrode, and then flush or remove the fragments.
Note: The discharge power needs to be controlled to avoid shock wave damage to the bile duct wall.
Ureteroscopic Lithotripsy (URS)
Application Scenario: Treatment of ureteral stones, especially middle and lower segment stones or when the holmium laser lithotripsy equipment is limited.
Operation Method: Introduce the liquid electrolithotomy probe through a rigid or flexible ureteroscope, and the electrode is close to the surface of the stone for discharge and crushing. When operating the soft endoscope, pay attention to the problem of reduced flushing fluid flow.
Historical Development: It was first reported in 1985 for ureteral stones, and there are fewer postoperative complications.
Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy (PCNL)
Application Scenario: Treatment of larger kidney stones (such as staghorn stones) or hard stones that are difficult to crush with ultrasonic lithotripsy.
Operation Method: After percutaneous establishment of a nephroscopic channel, use a liquid electrolithotomy electrode to crush the stones in the renal pelvis or calyx. Rapid flushing fluid flow is required to prevent the electrode from overheating.
Note: The electrode needs to be kept 5-10mm away from the nephroscope objective to avoid damaging the lens.
Electrohydraulic Lithotripsy for Bladder Stones
Application Scenarios: Treatment of large bladder stones, especially for patients who cannot tolerate open surgery.
Historical Background: First used for bladder stones in 1955, and then gradually extended to other cavities.
Technical Points: It needs to be operated in a liquid medium, usually using saline as the medium.
Choledochoscope Lithotripsy
Application Scenarios: Used for residual stones or impacted stones after biliary surgery.
Operation Method: The electrohydraulic lithotripsy electrode is inserted through the working channel of the choledochoscope, and the stone is flushed or removed after lithotripsy under direct vision.
Advantages: High success rate (96% lithotripsy rate), reducing the risk of secondary surgery.
Core Advantages and Risks of Electrohydraulic Lithotripsy Technology
Advantages: Low equipment cost, flexible probe (minimum 1.6Fr), suitable for hard stones.
Risk: It may cause bile duct perforation and bleeding, and the discharge direction and power must be strictly controlled.
Why Choose Us?
Full Industry Chain Collaboration Capabilities
Own key component production base to ensure supply chain security.
Provide one-stop seamless connection service from prototype development → registration test samples → mass production.
Forward-Looking Layout of Clinical Transformation
Provide a full set of technical information support for product registration
Provide animal experiment data package services to accelerate the clinical enrollment of customer products
Co-organize innovation laboratories with universities
Patent Technology Support
Hold a number of core technology patents in the optoelectronic field (covering liquid electrolithotomy, plasma, pulse control algorithm, electrode sealing structure, etc.)
100% independent intellectual property rights of the shock wave generation module, support secondary development to avoid property rights disputes
- https://www.smartveingroups.net/how-to-create-differentiated-competitiveness-for-medical-enterprises.html