While the mechanical robustness of Isuzu engines is legendary, their reliable operation hinges just as critically on the health of their electrical systems. The starter and the generator (often referred to as an alternator) are the two pillars of this system, responsible for initiating engine operation and sustaining its electrical needs. Failure in either of these components leads to immediate downtime, disrupting operations and potentially causing cascading electrical issues. This article provides an expert guide to the essential maintenance of starters and generators for Isuzu engines, detailing how proactive care and the use of quality spare parts are key to preventing electrical malfunctions and ensuring the consistent reliability of your heavy equipment.
The Critical Roles of the Starter and Generator in Isuzu Engines
Understanding the function of each component highlights the importance of their maintenance:
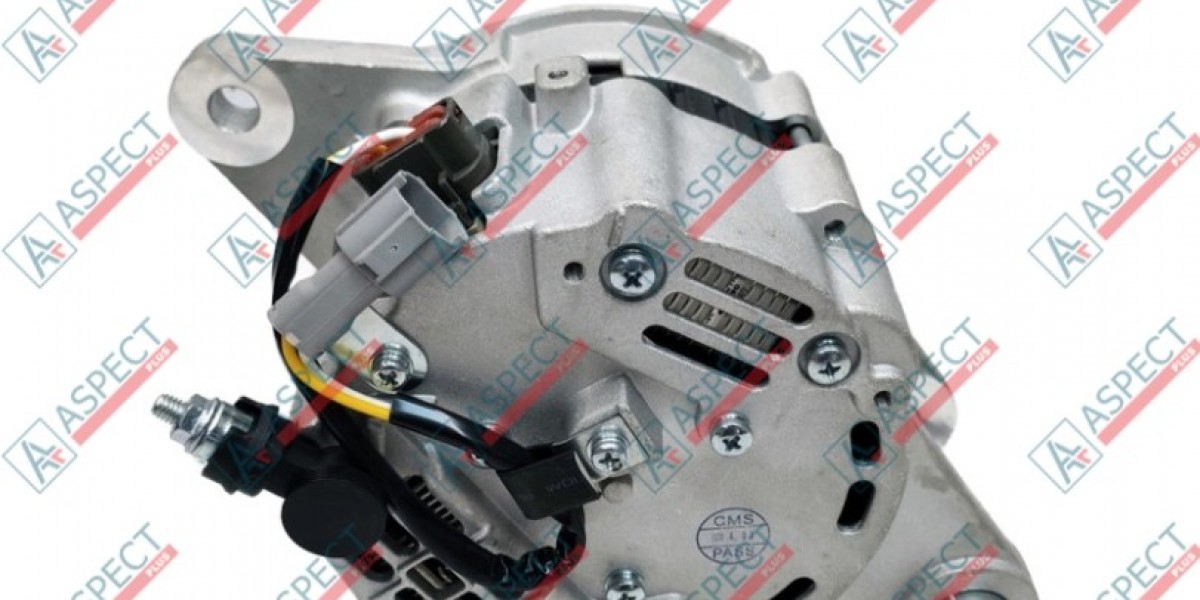
The Starter Motor: This powerful electric motor draws high current from the battery to rotate the engine's flywheel, initiating the combustion process. Its operation is brief but intense, subjecting it to significant electrical and mechanical stress. Key parts include the motor windings, brushes, bearings, and the solenoid (which engages the starter drive).
The Generator (Alternator): Once the Isuzu engine is running, the generator takes over. Driven by a belt from the crankshaft, it produces electrical energy to recharge the battery and power all the vehicle's or equipment's electrical systems (lights, ECU, sensors, cabin accessories). Critical components include the rotor, stator, diodes (rectifier), voltage regulator, bearings, and brushes (in some designs).
Failure in either component brings the machine to a halt.
Common Causes of Starter and Generator Malfunctions
Electrical failures in Isuzu engines often stem from wear, contamination, or external factors impacting these key components.
Starter Issues:
Worn Brushes: Carbon brushes conduct electricity to the rotating armature. They wear down over time, leading to poor contact and failure to crank.
Solenoid Failure: The solenoid acts as a heavy-duty switch and engages the starter drive gear. Corrosion or internal winding failure prevents engagement or power delivery to the motor.
Bearing Wear: Worn bearings cause misalignment of the armature, leading to grinding noises and eventual seizure.
Wiring/Connection Problems: Loose or corroded battery cables or connections to the starter/solenoid prevent sufficient current flow.
Generator Issues:
Voltage Regulator Failure: This component controls the generator's output voltage. Failure can lead to undercharging (dead battery) or overcharging (damaging the battery and electronics).
Diode Rectifier Failure: Diodes convert AC current generated by the stator into DC current. Failed diodes result in significantly reduced charging output.
Bearing Failure: Worn bearings cause a whining noise and can eventually lead to rotor/stator damage or seizure.
Worn Brushes/Slip Rings (if applicable): Similar to starters, these wear down, causing poor electrical contact.
Belt Problems: A loose, worn, or broken drive belt prevents the generator from spinning at the correct speed, leading to no or low charge.
Preventive Maintenance Checklist for Isuzu Starters and Generators
Proactive maintenance is the most effective strategy for preventing electrical malfunctions.
Battery Health is Paramount:
Keep Terminals Clean: Regularly clean battery posts and cable clamps to ensure solid, low-resistance connections. Corrosion is a major cause of starting problems.
Check Charge & Condition: Ensure the battery is adequately charged and test its health periodically. A weak battery puts immense strain on the starter motor.
Visual Inspections (Wiring & Connections):
Check Tightness: Regularly inspect all main power cables (battery to starter, engine ground, generator output) for tightness. Loose connections cause high resistance and heat.
Inspect for Damage: Look for chafed, cracked, or corroded wiring on both the starter and generator circuits. Repair or replace damaged sections immediately.
Generator Belt Maintenance:
Check Tension: Ensure the generator drive belt has the correct tension specified in the Isuzu service manual. A loose belt slips, reducing charging output; too tight, and it damages bearings.
Inspect Condition: Look for cracks, fraying, or glazing on the belt. Replace worn belts promptly.
Listen for Abnormal Noises:
Starter: A grinding sound during cranking indicates worn drive gear teeth or bearing issues. A rapid clicking sound often points to low battery voltage or a faulty solenoid.
Generator: A high-pitched whining noise usually signals failing bearings.
Keep Components Clean: Dirt, oil, and grease buildup can trap heat and interfere with electrical connections. Keep the starter and generator casings relatively clean.
Diagnostics: Identifying the Source of the Problem
When an electrical issue arises, systematic diagnostics is key.
Starter Issues:
No Crank/Clicking: Usually points to a battery issue, poor connections, or a faulty solenoid. Start by testing battery voltage and cleaning all connections.
Slow Cranking: Often indicates a weak battery, high resistance in the cables, or internal starter motor wear (brushes/bearings).
Starter Spins but Engine Doesn't Crank: Suggests a problem with the starter drive mechanism or solenoid engagement.
Generator Issues:
Battery Warning Light On: The most obvious sign of a charging system fault.
Dim Lights/Slow Accessories: Indicates the generator is not producing enough power, and the system is running off the battery.
Low System Voltage: Use a multimeter to check the voltage at the battery terminals with the engine running (should typically be 13.8-14.5V). Low voltage confirms a charging problem. Further tests can isolate whether the issue is the generator itself, the regulator, or wiring.
The Importance of Quality Spare Parts
When replacing components like solenoids, voltage regulators, brushes, or bearings, the quality of the spare parts is critical for long-term reliability.
Material and Manufacturing Standards: Genuine Isuzu electrical parts or high-quality certified analogues are made with materials designed to handle the high currents and temperatures involved. Inferior materials in brushes or windings will wear out quickly or fail under load.
Precision Fit: Components like bearings must meet exact dimensional tolerances. Low-quality parts can lead to misalignment and premature failure.
Ensuring Longevity: Using quality parts minimizes the risk of repeat failures, ensuring the longevity of both the repaired component and the overall Isuzu engine electrical system.
Our company Aspect Plus offers a wide range of genuine Isuzu parts and quality spare parts for starters, generators, and related electrical systems, ensuring your maintenance efforts lead to lasting reliability.
Conclusion
Preventing electrical malfunctions in Isuzu engines relies on a combination of diligent preventive maintenance and the strategic use of quality spare parts. Regular attention to battery health, wiring integrity, belt condition, and listening for warning signs can avert many common starter and generator failures. When repair is necessary, investing in genuine Isuzu electrical parts or certified high-quality alternatives is the only way to guarantee the restored performance, reliability, and longevity of your heavy equipment's vital electrical systems.
For expert advice on Isuzu engine maintenance, professional diagnostics, and a reliable source for quality Isuzu parts, contact the specialists at Aspect Plus.